ASP.NET Core course in Chennai
Introduction to ASP.NET Core course in Chennai:
There are various respected colleges in Chennai that offer comprehensive ASP.NET Core training courses.
The course provides hands-on experience through real-world projects, preparing you to tackle web development issues confidently.
An ASP.NET course equips you with the tools and knowledge to become proficient in building web applications using Microsoft’s robust ASP.NET framework.
The course covers ASP.NET basics and architecture, gradually progressing to advanced topics like data management, security, and performance optimization.
Special features of the ASP.NET Core course in Chennai:
ASP.NET is a constantly growing technology, and this course will keep you up to date on the latest breakthroughs and industry trends, increasing your value in the job market.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced developer, the Basics of ASP.NET course caters to a wide range of skill levels and provides a thorough learning experience.
What type of hands-on experience does the ASP.NET Core course provide in Chennai?
- Web application development with ASP.NET
- Create interactive online forms.
- Integration and modification of databases
- Authentication and authorization of users
- Implementation of MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture
Key Benefits of the ASP.NET Core course in Chennai:
Prepare to enter into the exciting world of ASP.NET!
Microsoft’s web development framework is a powerful tool for building strong and dynamic websites and apps.
Offering an array of tools and features, ASP.NET caters to beginners and seasoned developers. At its core, ASP.NET Overview is a server-side framework ideal for crafting dynamic websites, apps, and services.
Its seamless integration with Microsoft technologies like SQL Server and Azure empowers the creation of scalable, high-performance applications.
ASP.NET stands out for its user-friendly nature. Building interactive web pages, from forms to data-driven apps, becomes a breeze with a range of controls and libraries.
Its drag-and-drop functionality expedites UI development, reducing both effort and errors. Performance is a highlight of ASP.NET.
Scope of ASP.NET Core course in Chennai:
The scope of an ASP.NET Core course in Chennai is highly promising, with several options in web development and beyond. Here’s a look at the size of an ASP.NET course:
Web Development Careers: Completing an ASP.NET course prepares you to create dynamic and interactive web apps. This opens the door to a variety of positions, including web developer, full-stack developer, front-end developer, and back-end developer.
Diverse areas: ASP.NET is used in e-commerce, banking, healthcare, entertainment, and other areas. This diversity broadens your opportunities to work in fields that correspond with your interests.
Many software organizations demand ASP.NET Core in Chennai to create web-based solutions for their clients, making you an important member of software development teams.
Corporate Intranets: Large firms frequently use ASP.NET to create internal applications and corporate intranets, providing chances for enterprise-level software development.
Freelancing: If you know ASP.NET and MVC, you can work as a freelance web developer, taking on projects from clients all over the world and enjoying the flexibility that comes with it.
Career Possibilities of Learning the ASP.NET Core course in Chennai:
Maria Academy in Chennai offers placement opportunities as an add-on to every student/professional who has completed our classroom or online training.
With experience, ASP.NET developers take on more complex projects, fostering a sense of professional growth and accomplishment.
ASP.NET developers experience the satisfaction of creating impactful and user-friendly web applications, seeing their work in action, and receiving positive user feedback.
ASP.NET is used by both large and small organizations, offering the chance to work with renowned companies that provide competitive salaries and significant growth prospects.
ASP.NET certification is your ticket to advancing your web development career.
Microsoft’s certification verifies your knowledge of how to use the ASP.NET framework for web applications.
Adding it to your resume enhances your marketability, showcasing your readiness to excel in the field.
Moreover, it unlocks diverse career paths, from web developer to technical lead, due to the high demand for ASP.NET skills.
Frequently asked questions:
1. Does Maria Academy provide placement?
We have excellent relationships with over 700+ top MNCs, including SAP, Oracle, Amazon, HCL, Wipro, Dell, Accenture, Google, CTS, TCS, and IBM.
More than 3500 students were placed last year in India and globally.
Maria Academy conducts development sessions including mock interviews, presentation skills to prepare students to face a challenging interview situation with ease.
2. Is Maria Academy certification good?
Certification is accredited by every major global company.
Maria Academy is a unique Authorized Oracle Partner, Authorized Microsoft Partner, Authorized Pearson Vue Exam Center, Authorized PSI Exam Center, and Authorized Partner Of AWS
3. Work On Live Projects?
The entire ASP.NET training has been built around real-time implementation. You get hands-on experience with industry projects, hackathons & lab sessions, which will help you to build your project portfolio
GitHub repository and showcase to recruiters in interviews, and get placed.
4. Who are the Trainers?
All Maria Academy’s trainers are industry practitioners with at least 9-12 years of relevant IT experience. They are subject matter experts and have been trained by Maria Academy to provide an excellent learning experience.
5. What is a web application?
A normal website is not the same as a web application. Websites are static. The website returns an HTML page when you visit it, without performing any processing to create the HTML page’s contents. Reloading the browser will display the same page. A web application, on the other hand, may give you a different answer each time you visit.
6. What is the NuGet package manager?
Not all code is created from scratch by software developers. They depend on code libraries created by other programmers.
A way for developers to download and utilize pre-existing libraries, sometimes known as packages, must be included in any contemporary development environment.
For instance, the NPM (Node Package Manager) in the JavaScript ecosystem allows developers to locate and utilize libraries created by other JavaScript developers.
If you are seeking for advanced course in .net web application, contact us at Asp.net core training
Introduction to Asp.Net core MVC Framework
In this article, I am excited to give you an overview of the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern and the ASP.NET Core MVC framework! MVC stands for Model, View and Controller.
ASP.NET Core MVC is a design pattern used to create the architecture. Together, can explore some interesting points about how they work.
Let us dive in!
ASP.NET Core MVC is a web framework for building modern, scalable, and high-performance web applications using the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern.
It is part of ASP.NET Core, an open-source, cross-platform framework developed by Microsoft.
Key features of ASP.NET Core MVC:
Model-View-Controller (MVC) Architecture
- Model: Represents the application’s data and business logic.
- View: Handles the UI and presentation logic.
- Controller: Manages user input, processes requests, and returns responses.
Cross-Platform
- Works on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Supports deployment on IIS, Docker, and cloud platforms.
Razor View Engine
- Uses Razor syntax (.cshtml) for dynamic HTML rendering.
- Provides strong typing with @model and @ViewBag.
Routing System
- Uses attribute-based and convention-based routing.
- Example: app.UseEndpoints (endpoints => { endpoints.MapControllerRoute(…); });
Dependency Injection (DI)
- Built-in support for dependency injection to manage services and components.
Tag Helpers & View Components
- Provides Tag Helpers for HTML elements (e.g., <form asp-action=”Login”>).
- View Components enable reusable UI logic.
Benefits of MVC ASP.NET CORE:
Testability
- ASP.NET Core MVC supports unit testing because of its decoupled architecture.
- Dependency Injection (DI) is built-in, making it easier to test individual components.
Cross-Platform Support
- ASP.NET Core is cross-platform, meaning you can deploy applications on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Performance and Optimization
- ASP.NET Core is faster than traditional ASP.NET due to features like:
- Optimized request processing
- Minimal overhead
- Asynchronous programming support (async/await)
- Built-in caching and middleware support to enhance speed.
Routing Flexibility
- Supports attribute-based routing, making route definitions more readable and manageable.
- Allows customization of URL structures for SEO-friendly URLs.
Built-in Dependency Injection (DI)
- ASP.NET Core MVC includes native DI support, making it easier to manage dependencies and improve modularity.
Security Features
- Built-in authentication and authorization (supports JWT, OAuth, Open ID, Identity, etc.).
- CSRF protection, XSS prevention, and anti-forgery tokens for secure applications.
Tag Helpers and Razor Views
- Tag Helpers make writing HTML in Razor views easier and more maintainable.
- Razor Pages (part of ASP.NET Core) simplify small-scale applications while still benefiting from MVC.
Modular Middleware Pipeline
- Unlike traditional ASP.NET, ASP.NET Core provides a lightweight and configurable request pipeline.
- Middleware can be customized and optimized for specific needs.
Integration with Modern Frontend Technologies
- Works well with React, Angular, Vue.js, and other SPA frameworks.
- Supports Web APIs for RESTful services.
Scalability and Cloud Support
- Easily deployable to cloud environments like Azure, AWS, or Google Cloud.
- Supports microservices and containerization (Docker, Kubernetes).
Open Source and Community Support
- ASP.NET Core is open source and backed by Microsoft and a large community.
- Frequent updates, bug fixes, and improvements.
Role of View in MVC ASP.NET CORE:
Presentation Layer
The View is primarily responsible for displaying the user interface.
It contains HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and Razor syntax (@) for embedding C# code.
Receives Data from Controller
The Controller prepares the data (usually from the Model) and passes it to the View using a View Model or strongly typed model.
Uses Razor Syntax
Razor syntax (@{ }, @Model, @Html.ActionLink, etc.) helps embed C# code inside the View to generate dynamic content.
Does Not Contain Business Logic
The View should not have any complex logic (like database queries or business rules). Instead, it should focus only on rendering data.
Supports Partial Views & Layouts
Reusable UI components can be created using Partial Views (@Html.Partial(), @Html.RenderPartial()).
A consistent UI structure can be maintained using Layout Views (_Layout.cshtml).
Helps in Client-Side Interactions
Views can include JavaScript, jQuery, or AJAX to enhance the user experience.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is MVC in ASP.NET?
MVC (Model-View-Controller) is a software design pattern used for developing web applications by separating concerns into three components:
- Model – Manages data and business logic.
- View – Handles the UI presentation.
- Controller – Manages user input and interacts with the Model and View.
What is the difference between MVC and Web API?
| Feature | MVC | Web API |
| Purpose | Builds web applications with Views (HTML) | Builds RESTful services (JSON/XML) |
| Return Type | View (HTML) or JSON | JSON or XML |
| Routing | Uses routes.MapRoute() | Uses config.Routes.MapHttpRoute() |
| Controllers | Controller base class | ApiController base class |
What are the advantages of using MVC in ASP.NET?
- Separation of concerns – Code is clean and well-organized.
- Testability – Supports unit testing due to the separation of logic.
- Scalability – Easily extendable and maintainable.
What is a Partial View in MVC?
A Partial View is a reusable view component (like a header, footer, or sidebar) that can be included in other views.
Example of Partial View Usage:
CsharpCopyEdit@Html.Partial(“_Header”)
What is the difference between ViewBag, ViewData, and TempData?
| Feature | ViewBag | ViewData | TempData |
| Type | Dynamic | Dictionary | Dictionary |
| Lifetime | Current request | Current request | Available across multiple requests (e.g., redirects) |
| Requires Type Casting? | No | Yes | Yes |
What is Dependency Injection in ASP.NET MVC?
Dependency Injection (DI) used to inject dependencies (services, repositories, etc.) into controllers instead of creating them manually.
Conclusion
MVC in ASP.NET provides a structured, flexible, and scalable framework for modern web applications. It improves performance, testability, and maintainability, making it an ideal choice for enterprise applications.
- The View in MVC is all about rendering UI.
- It receives data from the Controller and displays it.
- Razor is used to dynamically generate HTML.
If you are seeking for advanced course in .NET web application, contact us at Asp.net core training
Understanding Encapsulation and Abstraction in C#
Two fundamental ideas in the field of object-oriented programming (OOP)—abstraction and encapsulation—are essential to creating reliable and maintainable software systems. Though they are not unique to C#, these ideas are central to the language’s architecture and are widely used in its framework and libraries. Let’s explore the meaning of abstraction and encapsulation in C# and how they help write cleaner code.
Encapsulation
A key component of object-oriented programming (OOP) in C# is encapsulation, which is the grouping of data and methods (or behaviours) that manipulate the data into a single unit called a class. Encapsulation provides controlled access to an object’s internal state through well-defined interfaces, like properties and methods, while shielding it from external manipulation and access.
Access Modifiers
Access modifiers in C# are used to manage a program’s types and members’ visibility and accessibility. By limiting the amount of access that other program components have to the encapsulated data and methods, these modifiers are essential to the encapsulation process.
- public: Any other code within the same assembly or another assembly that references it can access the member.
- private: Only members of the same class or struct may access this member.
- Protected: The member can be accessed by derived classes and by other members of the same class or struct.
- Internal: Only those in the same assembly can access the member.
- safe internal: The member can be accessed through derived classes or within the same assembly.
Properties
In C#, properties provide regulated access to a class’s private fields by encapsulating them. They guarantee data integrity by enabling data validation and manipulation prior to access or modification.
public class Person
{
private string name;
public string Name
{
get { return name; }
set
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(value))
{
name = value;
}
else
{
throw new ArgumentException("Name cannot be empty");
}
}
}
}
Methods
Methods contain an object’s behaviour. They have the ability to act or perform operations on the internal state of the object and return results.
public class Calculator
{
public int Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
}
Advantages of Encapsulation
- Data Hiding: Encapsulation ensures data integrity by preventing unauthorized manipulation and concealing an object’s internal state from external access.
- Abstraction: By encapsulating an object, developers can concentrate on its behaviour’s key components rather than worrying about the intricacies of its internal implementation.
- Modularity: By combining related data and methods into a single unit, encapsulation encourages modularity and makes the codebase simpler to comprehend and manage.
- Code Reusability: Encapsulation makes code reuse easier by offering clearly defined interfaces that let objects be used in various contexts without needing to be modified.
To summarize, encapsulation in C# is a powerful mechanism for developing robust and maintainable software systems by hiding objects’ internal complexity and providing controlled access to their state and behaviour via well-defined interfaces. It encourages code organization, reuse, and dependability, making it a critical concept in modern software development.
Abstraction
A key component of object-oriented programming (OOP) in C# is abstraction, which is displaying only an object’s essential features while concealing the intricate implementation details of a system. It enables developers to concentrate on an object’s functionality rather than its implementation. Creating a blueprint for objects with shared traits and behaviours can be accomplished through abstraction, all without having to define each object’s precise implementation.
Abstract Classes and Methods
Abstract classes and methods are commonly utilized in C# to accomplish abstraction. A class that lacks the ability to be instantiated directly and that might include one or more abstract methods that are declared but not implemented is known as an abstract class. Specific functionality is meant to be implemented by derived classes through the use of abstract methods.
public abstract class Shape
{
public abstract void Draw(); // Abstract method
}
public class Circle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
// Implementation for drawing a circle
}
}
public class Rectangle : Shape
{
public override void Draw()
{
// Implementation for drawing a rectangle
}
}
Interfaces
Interfaces are another tool in C#’s toolkit for achieving abstraction. A contract that classes can implement is defined by an interface. It has no implementation details and only method signatures, properties, events, or indexers. All of the members defined in an interface must have implementations available in any class that implements that interface.
public interface IShape
{
void Draw(); // Method signature
}
public class Circle : IShape
{
public void Draw()
{
// Implementation for drawing a circle
}
}
public class Rectangle : IShape
{
public void Draw()
{
// Implementation for drawing a rectangle
}
}
Benefits of Abstraction
- Flexibility: By defining common interfaces and behaviors that multiple classes can implement, abstraction makes it possible to write extensible and flexible code.
- Code Reusability: Developers can promote code reusability by defining abstract classes or interfaces, which allow code to be reused across various application components.
- Maintenance: By enabling modifications to be made to the underlying implementation without impacting the external interface accessible to other areas of the codebase, abstraction makes maintenance easier.
- Encapsulation: Since encapsulation exposes only the functionalities that are absolutely necessary while hiding the internal workings of an object, abstraction and encapsulation frequently go hand in hand.
In conclusion, abstraction in C# offers a strong tool for encouraging code reuse, controlling complexity, and creating modular, maintainable software systems. By delegating the specific implementation details to the individual classes that inherit from abstract classes or implement interfaces, it allows developers to concentrate on creating concise and clear interfaces.
Benefits of Abstraction and Encapsulation
- Modularity: Objects can be treated as black boxes, allowing changes to be made to one part of the system without affecting others.
- Code Reusability: Abstraction enables the creation of generic components that can be reused across different parts of the application.
- Security: Encapsulation prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data and provides a controlled interface for interacting with it.
- Maintainability: By hiding implementation details, abstraction and encapsulation make code easier to understand, debug, and maintain.
In conclusion, abstraction and encapsulation are essential principles in C# programming that promote code organization, flexibility, and reliability. By properly abstracting functionality and encapsulating data, developers can create robust and scalable software systems that are easier to understand, maintain, and extend.
Dot Net Web API Online class
Introduction to Dot Net Web API:
Microsoft offers a framework called Dot Net Web API (Application Programming Interface) that allows developers to create HTTP services that are accessible to a variety of clients, such as web browsers, mobile devices, and Internet of Things gadgets. It is a component of the broader.NET framework and is made especially to make use of the ASP.NET technology stack to facilitate the development of RESTful (Representational State Transfer) APIs. A Web API is fundamentally a group of HTTP endpoints, or URIs, that receive requests over HTTP and respond with HTTP. These endpoints enable clients to carry out CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on data; they typically correlate to resources or actions within your application.
Why Should You learn Dot Net Web API Online:
Learning Dot Net Web API is not only beneficial, but also necessary for both experienced and novice developers in the modern digital world. Proficiency in developing strong APIs using Microsoft’s.NET framework has become a valuable skill set in the tech industry due to the growing demand for web-based apps and services.
Enrolling in an online Dot Net Web API course could be your ticket to success, regardless of your level of experience with programming. Beginners looking to get started or professionals looking to advance your knowledge should both benefit from this course. These are the reasons why:
- Extensive Curriculum: An excellent online course will provide a thorough curriculum that addresses every facet of developing Dot Net Web APIs. You will delve deeply into the nuances of creating scalable and secure APIs, from comprehending RESTful principles to putting authentication and authorization into practice.
- Practical Training: Getting your hands dirty is the best way to become an expert at Dot Net Web API. Interactive tutorials, coding exercises, and real-world projects are common features of online classes that let you put your newly acquired knowledge to use in a real-world situation. This approach to learning through experience guarantees that you will not only understand theoretical ideas but also become proficient in writing code and resolving real-world problems.
- Flexible Schedule: One of the main benefits of taking classes online is being able to set your own hours. All types of learners—full-time, working professionals, and those with demanding schedules—are able to access course materials and take part in lectures at their own convenience and pace. With this flexibility, the limitations of traditional classroom-based learning are removed, allowing you to successfully balance your academic goals with other obligations.
- Professional Advice: Taking an online course gives you access to knowledgeable instructors who have years of experience developing Dot Net Web APIs. These instructors offer insightful advice, direction, and mentorship throughout your learning process by bringing their extensive knowledge and professional experience to the virtual classroom. Their knowledge guarantees that you will obtain excellent instruction and remain current with the newest trends and best practices in API development.
- Community Support: Students who take online classes frequently establish a thriving online community with a shared love of technology. In addition to improving your educational experience, interacting with other students in discussion boards, group projects, and cooperative activities opens up networking opportunities and strengthens bonds within the tech community.
What Our Training Provides:
- Comprehensive Curriculum: Our training covers the entire breadth of .NET and web API, from fundamental ideas to advanced topics, preparing you for real-world projects.
- Hands-on tasks: Gain practical experience by completing real-world tasks and applying what you’ve learned during the course.
- Flexibility: Our online approach allows you to learn at your own pace, accommodating your hectic schedule.
- Interactive Learning: Participate in interactive workshops, discussions, and Q&A sessions to better your comprehension and obtain answers to any issues you may have.
- Professional Teachers: Learn from industry experts with extensive .NET programming experience and receive valuable insights.
Who should take the Course:
- IT specialists seeking professional development.
- Aspiring programmers
- Web Designers
- Software Developers
Conclusion:
In conclusion, anyone hoping to succeed in the software development industry would be well advised to take up a Dot Net Web API online course. Gaining expertise in Dot Net Web API opens up a world of opportunities in the rapidly changing technology landscape, regardless of your goals—creating your own web applications, advancing your career, or starting a new professional journey.
Why then wait? Enroll in an online course on Dot Net Web API now to start the process of learning this crucial skill set, which will launch your career to new heights.
If you need any Training / Technical Support in DOTNET & SQL Contact +91 90427 10472
Understanding Microsoft Azure Fundamentals
Microsoft Azure has become a prominent platform in the cloud computing space, providing a wide range of services to individuals, companies, and organizations globally. It is becoming more and more important for businesses to grasp the foundations of Microsoft Azure as they move their operations to the cloud. The purpose of this article is to give a general overview of Azure, including its essential features, advantages, and the reasons behind its rise to prominence in the cloud computing industry.
What is Microsoft Azure?
Microsoft offers a full-featured cloud computing platform called Microsoft Azure. Computing, storage, networking, databases, machine learning, Internet of Things (IoT), and other services are among the many that it provides. With Azure, users can create, launch, and maintain services and applications via Microsoft’s extensive global data centre network.
Key Components of Microsoft Azure:
- Compute: For high-performance computing (HPC) workloads, Azure offers a variety of computing options, such as virtual machines (VMs), containers, serverless computing with Azure Functions, and Azure Batch.
- Storage: Blob Storage for unstructured data, File Storage for cloud file sharing, Queue Storage for messaging between application components, and Disk Storage for virtual machines (VMs) are just a few of the scalable storage options that Azure provides.
- Networking: Users can establish virtual networks, link load balancers to Azure, connect on-premises data centers to Azure, and guarantee secure communication by utilizing Azure VPN Gateway and Azure ExpressRoute features.
- Databases: Azure offers a range of database services, such as Cosmos DB for globally distributed NoSQL databases, Azure SQL Database for relational databases, Azure Database for MySQL and PostgreSQL, and services like Azure Synapse Analytics and Azure Cache for Redis.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Microsoft’s cloud-based identity and access management service, Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), enables users to safely log in and access resources.
- AI and Machine Learning: To create, train, and implement machine learning models, Azure provides AI and Machine Learning services like Azure Machine Learning, Azure Cognitive Services, and Azure Databricks.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Services like Azure IoT Central offer an end-to-end IoT application platform, while Azure IoT Hub facilitates safe and scalable connectivity between IoT devices and the cloud.
- Developer Tools: For continuous integration, delivery, and testing, Azure offers a comprehensive range of developer tools and services, such as Azure DevOps, Visual Studio Team Services, and Azure DevTest Labs.
Benefits of Microsoft Azure:
- Scalability: Azure enables companies to adjust their resource levels in response to demand, guaranteeing peak efficiency and optimum performance.
- Global Reach: Azure allows businesses to deploy applications closer to their users for lower latency and an enhanced user experience. Azure has data centers situated in various regions of the world.
- Security and Compliance: Azure guarantees data protection and regulatory compliance across a range of industries by adhering to industry-standard security practices and compliance certifications.
- Cost-effectiveness: Azure provides pay-as-you-go pricing options that spare companies from up-front capital costs by letting them pay only for the resources they really use.
- Integration: Azure offers a seamless ecosystem for application development and management by integrating with other Microsoft products and services, as well as third-party tools and technologies.
Conclusion:
As a key player in the cloud computing space, Microsoft Azure enables enterprises to grow, innovate, and completely reinvent themselves. For people and companies hoping to take full advantage of cloud computing, knowing the foundations of Azure is crucial. Azure is still the go-to option for cloud computing solutions in a variety of industries thanks to its extensive service portfolio, global presence, and dedication to security and compliance.
If you need any Training / Technical Support in DOTNET & SQL Contact +91 90427 10472
Caching in ASP .NET Core:
Introduction:
Effective data caching techniques are critical to improving the performance of web applications in the modern digital environment, where speed and scalability are critical requirements. The robust caching features of Microsoft’s open-source, cross-platform ASP.NET Core framework can greatly increase the scalability and responsiveness of web applications. We’ll examine the advantages, methods for implementation, and best practices of caching in ASP.NET Core in this article.
The Advantages of Caching in ASP.NET Core:
Caching stores frequently accessed data temporarily, reducing the need to retrieve it from its original source repeatedly. In ASP.NET Core, caching provides several advantages, including:
- Enhanced Performance: Caching lowers the latency involved in retrieving data from its original source by keeping frequently accessed data in memory, giving users faster response times.
- Decreased Database Load: By providing cached data rather than querying the database for each request, caching helps reduce the strain on the database server and increase system scalability.
- Improved Scalability: ASP.NET Core apps are more responsive and scalable when they use caching to manage more concurrent users and requests without sacrificing performance.
Types of Caching in ASP.NET Core:
Different caching mechanisms that meet different needs and scenarios are supported by ASP.NET Core. Several frequently utilized types of caching include:
- In-Memory Caching: This technique keeps data in the memory of the application so that it is easily accessible to queries made later. For storing small to medium-sized data sets that are accessed frequently, this kind of caching is appropriate.
- Distributed Caching: With distributed caching, data that has been cached can be shared between several applications or even between various web farm servers. Support for distributed caching with providers like Redis, SQL Server, or NCache is integrated into ASP.NET Core.
- Response Caching: This technique allows the entire HTTP response to be cached, including the status codes, HTTP headers, and HTML content that is generated. For content that can be cached at the HTTP level and is static or semi-static, this kind of caching is perfect.
Implementing Caching in ASP.NET Core:
Developers can take the following actions to take advantage of caching in ASP.NET Core:
- Configure Caching Services: Use the AddMemoryCache() or AddDistributedMemoryCache() methods to register caching services for either distributed or in-memory caching in the dependency injection container of the ASP.NET Core application.
- Install Caching Middleware: To enable response caching, add caching middleware to the application’s request processing pipeline by either implementing custom middleware for more granular control or by using the UseResponseCaching() method.
- Decorate Cached Resources: To define caching policies, such as cache duration, cache location, and cache profiles, decorate controller actions or Razor pages with caching attributes like [ResponseCache].
Best Practices for Caching in ASP.NET Core:
The following best practices should be taken into consideration in order to optimize the advantages of caching while avoiding typical pitfalls:
- Use Caching Wisely: Only store in cache data that is likely to be frequently retrieved or computed at a high cost. Refrain from over-caching or caching frequently changing volatile data.
- Track Cache Performance: To guarantee optimal cache performance and avoid memory-related problems, track cache hit rates, eviction rates, and memory usage.
- Use Cache Invalidation: Use cache expiration policies or manual cache invalidation mechanisms, among other cache invalidation techniques, to guarantee that data in the cache is accurate and current.
Conclusion:
Caching is a potent method for enhancing ASP.NET Core applications’ responsiveness, scalability, and performance. Developers can greatly lower latency, lessen database load, and improve user experience by utilizing caching mechanisms like in-memory caching, distributed caching, and response caching. To optimize its advantages while averting any potential downsides, caching must be used sparingly and in accordance with best practices. Because caching is a fundamental component of optimization strategies, ASP.NET Core applications can easily scale to meet the demands of contemporary online environments while delivering lightning-fast performance.
How to Host DOTNET site in IIS
what is IIS?
IIS, or Internet Information Services, is a web server software developed by Microsoft for hosting and serving web applications and websites. It is an integral part of the Windows Server operating system and is widely used for deploying and managing web-based applications on the Microsoft platform.
Key features of IIS include:
Web Server Functionality: IIS serves as a powerful web server, handling HTTP and HTTPS requests. It supports various web technologies, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and different server-side scripting languages like ASP.NET.
Application Hosting: IIS is designed to host and manage web applications and services built on the Microsoft technology stack, such as ASP.NET, .NET Core, and PHP. It also supports classic ASP (Active Server Pages).
Security: IIS provides robust security features, including authentication, authorization, and SSL/TLS support for encrypting data in transit. It allows administrators to control access to websites and applications based on user roles and permissions.
Scalability: IIS is scalable and can handle a large number of concurrent connections. It supports load balancing and can be configured to distribute incoming requests across multiple servers for improved performance and reliability.
Management Tools: IIS comes with a user-friendly management interface, known as IIS Manager, which allows administrators to configure and manage web server settings, applications, and security features. It also supports remote administration.
Logging and Monitoring: IIS generates logs that provide detailed information about web server activity, helping administrators troubleshoot issues and analyze performance. Additionally, administrators can use performance monitoring tools to track server metrics.
Extensibility: IIS is extensible and supports the integration of various modules and extensions. This allows developers and administrators to add custom functionality, such as URL rewriting, compression, and caching.
FTP Server: In addition to its web server capabilities, IIS includes a built-in FTP (File Transfer Protocol) server, allowing users to transfer files to and from the server.
IIS is a versatile and widely used web server that caters to a broad range of web hosting needs, from simple static websites to complex dynamic web applications. It is a crucial component for organizations leveraging Microsoft technologies in their web development and hosting environments.
Hosting a .NET site in Internet Information Services (IIS) – Introduction:
Hosting a .NET site in Internet Information Services (IIS) is a crucial step in deploying web applications built on the .NET framework. IIS provides a robust and scalable platform for hosting, managing, and securing web applications. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of hosting a .NET site in IIS.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Host a .NET Site in IIS:
Step 1: Install IIS on the Server:
Before hosting a .NET site in IIS, ensure that IIS is installed on the server. You can install IIS through the Windows Features menu. Go to Control Panel -> Programs -> Turn Windows features on or off, and then select Internet Information Services.
Step 2: Install the Appropriate .NET Runtime:
Ensure that the server has the correct version of the .NET runtime installed to support your .NET application. You can download and install the necessary runtime from the official Microsoft website.
Step 3: Publish the .NET Application:
Publish your .NET application using Visual Studio or the command line. This process generates the necessary files for deployment. Choose the appropriate publish settings, including the target framework and deployment configuration.
Step 4: Create a New IIS Site:
Open the IIS Manager and create a new site for your .NET application. Right-click on “Sites” and choose “Add Website.” Enter a unique site name, set the physical path to the location where you published your .NET application, and assign a port number and host name if necessary.
Step 5: Configure Application Pool:
Create a new application pool or use an existing one for your .NET site. Ensure that the application pool is configured to use the correct version of the .NET runtime and is set up with the necessary permissions.
Step 6: Adjust Security Settings:
Review and adjust the security settings for your site. Configure authentication, authorization, and SSL settings based on your application’s requirements. Ensure that the necessary permissions are granted to the application pool identity.
Step 7: Test Your Site:
After configuring IIS, test your .NET site by navigating to the specified URL in a web browser. Ensure that all pages and functionalities work as expected. Monitor the IIS logs for any errors or issues.
Step 8: Monitor and Maintain:
Regularly monitor the performance of your .NET site in IIS. Use tools like Performance Monitor to analyze server metrics and address any performance bottlenecks. Keep the server and IIS components up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
Conclusion:
Hosting a .NET site in IIS involves several essential steps, from installing IIS and the correct .NET runtime to configuring application pools and security settings. Following this step-by-step guide will help you successfully deploy and manage your .NET web application in a secure and scalable environment.
Full Stack Dot NET Developer Course Online
Introduction
Full Stack.NET Developers play an important role in creating end-to-end solutions by seamlessly integrating front-end and back-end technologies using the Microsoft.NET framework. With the convenience of online courses, aspiring developers can begin their journey to master the complexities of Full Stack.NET development. This article serves as a guide, delving into the key components and benefits of online courses designed to develop skilled Full Stack.NET developers.
A Comprehensive Approach to Understanding Full Stack.NET Development
Using Microsoft’s.NET technologies, full stack.NET development includes both front-end and back-end development. For server-side development, it requires knowledge of languages like C# and ASP.NET, and for client-side development, frameworks like Angular or React. A wide range of topics are covered in online courses designed specifically for Full Stack.NET Developers, guaranteeing a well-rounded skill set.
Key Features of Online Full Stack.NET Courses:
Full Stack.NET Developers must have a strong understanding of C#. Online courses frequently begin with in-depth C# programming modules that cover topics such as object-oriented programming, data types, and control structures.
Courses cover ASP.NET MVC (Model-View-Controller), a framework for developing scalable and maintainable web applications. Students learn about routing, controllers, views, and data models while gaining practical experience in developing robust server-side applications.
Full Stack.NET Front-end developers must be knowledgeable about these technologies. HTML, CSS, and JavaScript are frequently used in online courses, as are popular front-end frameworks such as Angular and React. This allows developers to create interactive and user-friendly interfaces.
Database integration is a critical component of full stack development. The courses cover SQL for database management as well as ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) tools such as Entity Framework, which allow developers to interact with databases seamlessly.
Full Stack.NET Developers frequently create and consume APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). Online courses teach students how to create RESTful APIs, which allow different web application components to communicate with one another.
Source Control and Deployment:
Version control systems (such as Git) and deployment strategies are critical for application collaboration and release. Courses provide insights into Git workflows and deployment techniques, allowing developers to manage projects more efficiently.
Benefits of Online Full Stack .NET Development Courses:
Flexibility:
Online courses allow students to balance their studies with other commitments. Asynchronous learning materials, like video lectures and interactive assignments, cater to a variety of learning styles.
Hands-On Projects:
Practical application is critical to skill development. Many online courses include hands-on projects and real-world scenarios, allowing students to put theoretical knowledge into practice.
Community Support:
Forums and discussion boards are common features of online platforms that foster a sense of community. Learners can connect with their peers, share their experiences, and ask for help from instructors and other students.
Industry-Relevant Content:
Reputable online courses are created with input from industry experts. They keep up with the latest trends and technologies, ensuring that students learn skills that are relevant to today’s job market needs.
Conclusion: Shaping Future Full Stack .NET Developers
Starting the journey to become a Full Stack.NET Developer with online courses provides a flexible and comprehensive learning experience. Aspiring developers can expect to learn how to design, implement, and maintain fully functional web applications, making them valuable assets in the ever-changing web development landscape. Individuals who are dedicated and take the right online course can turn their coding passion into a rewarding career as a Full Stack.NET Developer.
If you need any Training / Technical Support in DOTNET & SQL Contact +91 90427 10472
Python in Web Development
INTRODUCTION:
Python web development is a popular and adaptable option for creating dynamic websites and web apps. A wide range of frameworks, modules, and tools are available for Python, which makes development easier and enables programmers to design scalable and effective web solutions.
It comprises designing, developing, and maintaining websites with a range of functions and uses by utilizing a variety of technologies, programming languages, and tools.
At its foundation, web development includes two essential aspects:
1. Front-end development
2. Back-end development
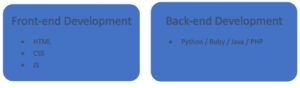
Front-end Development:
The visual and interactive components of a website that visitors interact with directly are the focus of front-end development. Using tools like HTML (Hypertext Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), and JavaScript, entails developing the layout, designing the user interface (UI), and implementing the visual components.
Back-end Development:
On the other hand, back-end development works with a website’s server-side functionality. It entails developing the architecture and logic needed to process data, manage database interactions, and maintain the operation of the website. Programming languages like Python, Ruby, Java, or PHP are used by back-end developers to create the server-side parts of websites.
WEB DEVELOPMENT USING PYTHON:
The process of developing websites and web applications with the Python programming language is known as Python web development. Python is a widely used and adaptable programming language that is well-known for its ease of use, readability, and extensive library and framework ecosystem.
Python is used by developers to construct server-side logic for web applications. This involves processing HTTP requests and responses, data storage and retrieval, business logic implementation, and dynamic content rendering.
SEVERAL ADVANTAGES TO USE PYTHON IN WEB DEVELOPMENT:
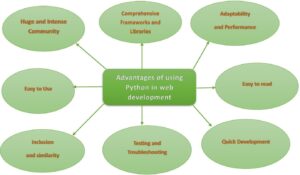
- Huge and Intense Community:
The Python community is large and vibrant, with many developers contributing to its development and providing assistance. Many tools, frameworks, and resources designed expressly for web development are available from the community. Python is a strong option for web development because of its wealth of community-driven tools and resources, which provide answers to a variety of needs.
- Comprehensive Frameworks and Libraries:
Python has a robust ecosystem of frameworks and tools that make web development chores easier. One of the most well-liked web frameworks for Python, Django, offers a sophisticated and comprehensive toolkit for creating intricate web applications. It is designed using the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural paradigm and comes pre-configured with features like URL routing, database ORM (Object-Relational Mapping), and authentication. Another lightweight and adaptable micro-framework that gives developers more control over the components and structure of an application is Flask. These frameworks, as well as others like Pyramid and Bottle, give web development a strong base and increase productivity.
- Adaptability and Performance:
Python is well-known for being performant and scalable, which makes it ideal for managing online applications with heavy traffic. Python frameworks like Django and asyncio can effectively manage concurrent requests and optimize server resources thanks to innovations like asynchronous programming. Furthermore, Python’s integration features make it simple to integrate with other languages, allowing programmers to use high-performance C or C++ libraries as necessary.
- Easy to read and use:
Python’s syntax is intended to be simple to understand and write, focusing on code readability and maintainability. Its simple syntax enables developers to express concepts in fewer lines of code, making development faster and more efficient. Python’s simplicity allows both new and experienced developers to work easily and collaboratively.
- Inclusion and Simplicity:
Python is adaptable for web development and interfaces with other technologies with ease. It supports a wide range of databases, including NoSQL databases like MongoDB and SQL-based databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite.
- Testing and Troubleshooting:
Python has strong testing frameworks that make developing and running tests for web applications easier, such unittest and pytest. Integrated development environments (IDEs) and pdb are two of the efficient debugging tools that enable developers to locate problems and solve them fast.
- Quick Development:
Python’s emphasis on productivity and simplicity makes it possible for developers to create web apps rapidly. Pre-built modules and libraries are readily available, allowing developers to take advantage of pre-existing solutions rather than having to start from scratch. Time-to-market is critical for startups and small-scale ventures, where this speedy development strategy is very helpful.
WEB DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORKS IN PYTHON:
Python offers several web frameworks to suit different needs and preferences. The following are a few well-known Python web development frameworks:
- Django
- Flask
- Pyramid
- Bottle
- CherryPy
- Tornado
WEB DEVELOPMENT LIBRARIES IN PYTHON:
Python web development provides an abundance of tools and frameworks to improve productivity and improve the development process. The following libraries & tools are frequently used in Python web development:
- Jinja2
- Pydantic
- Redis-py
- PyJWT
- Flask-WTF
- Flask-SQLAlchemy
- Celery
- SQLAlchemy
- Pillow
- Beautiful Soup
- Requests
ROADMAP FOR PYTHON WEB DEVELOPMENT:
A road map for using Python to construct websites that highlights the main ideas and procedures involved:
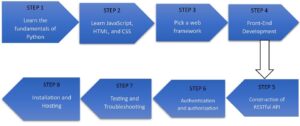
- Learn the fundamentals of Python:
Learn the syntax, data types, control structures, and functions that are essential to Python programming. To begin started, you can consult books or internet guides.
- Learn JavaScript, HTML, and CSS:
Get a fundamental knowledge of web technologies, like JavaScript for client-side interactivity, CSS for styling, and HTML for markup. These are required to understand and design websites.
- Pick a web Framework:
Choose a Python web framework based on the needs of your project. A few well-liked choices are Pyramid, Flask, and Django.
- Front-end Development:
Develop your web development abilities by being familiar with well-known front-end frameworks and modules like Angular, Vue.js, and React.
- Construction of RESTful API:
Create APIs that provide data and functionality to other apps or front-end interfaces using the web framework of your choice.
- Authentication and Authorization:
Learn how to use the built-in capabilities or extensions of your web framework to develop secure user registration, login, and access control techniques.
- Testing and Troubleshooting:
Become an expert at testing your websites. Find out more about end-to-end, integration, and unit testing. To write and run tests, use tools such as pytest, Python’s Selenium, or the testing frameworks included with your preferred web framework.
- Installation and Hosting:
Find out how to put your web application on a cloud platform or web server. Gain an understanding of ideas like scalability, security considerations, deployment automation, and server setup. For hosting web applications, platforms like Heroku, AWS, or PythonAnywhere are frequently utilized.
CONCLUSION:
Python is a powerful language that is well-suited for web development, which involves developing websites and web apps. Because of its ease of use, readability, and robust environment, Python is a great option for web development projects. Python offers a strong basis for web development, making it possible for programmers to create feature-rich, scalable websites quickly.
Comparing Java, C#, and Python: A Top N Comparison
Java, C#, and Python are three popular programming languages, each with distinct strengths, use cases, and features. Here’s a brief overview of the main differences between Java, C#, and Python.
Syntax:
- Java: Java uses a syntax similar to C++ and C. It enforces strict typing, and the syntax is intended to be readable and simple.
- C#: C# syntax is influenced by C++ and Java, but it incorporates features such as properties and events. It is primarily used for Windows development and works well within the Microsoft ecosystem.
- Python: Python is well-known for its clean and readable syntax. It uses indentation to indicate code blocks, which makes it visually distinct. Python focuses on code readability and simplicity.
Typing System:
- Java: Java is statically typed, which means that variable types must be declared before compilation.
- C#: C# is statically typed, like Java, and requires explicit type declarations.
- Python: Python is dynamically typed, which provides more flexibility by determining variable types at runtime.
Platform and Ecosystem:
- Java: The “Write Once, Run Anywhere” (WORA) principle underpins Java’s platform independence. It has a large ecosystem of libraries and frameworks and is popular for enterprise applications and Android development.
- C#: C# is inextricably linked to the Microsoft ecosystem, as it is widely used in Windows development and applications. It is the primary language for creating applications using the .NET framework.
- Python: Python is a versatile programming language with strong applications in web development, data science, artificial intelligence, and automation. It has a large collection of libraries and frameworks.
Memory Management:
- Java: Java manages memory automatically, which makes it easier for developers because they don’t have to deallocate or allocate memory explicitly.
- C#: C#, like Java, relies on garbage collection for memory management.
- Python: Python also uses automatic memory management, which is handled by a garbage collector.
Use Cases:
- Java: Commonly used in enterprise-level applications, Android app development, and large-scale systems.
- C#: Typically used for Windows applications, web development with ASP.NET, and game development with Unity.
- Python: Popular in web development (Django, Flask), data science (NumPy, Pandas), machine learning (TensorFlow, PyTorch), and automation.
Community and Popularity:
- Java: Java has a large and mature community with a long history, making it one of the most widely used languages.
- C#: C# has a strong community, particularly within the Microsoft ecosystem, and is widely used in enterprise settings.
- Python: Python has a thriving and diverse community, and it is one of the most popular programming languages worldwide.
Learning Curve:
- Java: Moderate learning curve, particularly for beginners. Strongly typed nature may necessitate more explicit code.
- C#: The learning curve is similar to Java, but with additional features such as LINQ.
- Python: The syntax is readable and concise, making it suitable for beginners.
Concurrency and Multithreading:
- Java: robust multithreading and concurrency support thanks to features like the java.util.concurrent package.
- C#: supports concurrency with the help of async/await features.
- Python: Parallelism may be constrained by Global Interpreter Lock (GIL), but asynchronous programming is possible with libraries like asyncio.
Performance:
- Java: generally has good Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation performance.
- C#: Performs competitively, especially when using the .NET runtime’s optimizations.
- Python: Because it’s interpreted, it’s typically slower than Java and C#, but compiled extensions can help with performance-critical tasks.
Integration with Other Technologies:
- Java: smooth interaction across a range of platforms and technologies.
- C#: outstanding compatibility with the Microsoft stack of technologies.
- Python: good compatibility with AI frameworks, data science tools, and web technologies.
In conclusion, the decision between Python, C#, and Java is based on the developer’s experience and preferences as well as the requirements of the project and the target platform. Every language has its advantages and works well for various kinds of applications.
Exploring New Development Trends in .NET and .NET Core
Introduction:
The field of software development is always changing, and the .NET ecosystem has seen significant shifts recently. Several trends in the .NET and .NET Core frameworks have emerged as developers adjust to new technologies and industry demands. In this piece, we examine the significant patterns that are influencing .NET development both now and in the future.
.NET 8 and Unified Platform:
Microsoft’s journey towards a unified platform is furthered with the release of .NET 8, which combines the best features of Xamarin, .NET Core, and .NET Framework. By offering a single codebase for applications targeted at various platforms, including Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS, Android, and more, this unified platform streamlines the development process.
.NET MAUI for Cross-Platform App Development:
Cross-platform application development is increasingly utilizing .NET MAUI (Multi-platform App UI) as the preferred framework. Developers can use a single codebase to create applications that run on Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS by utilizing .NET MAUI. This improves code reuse and streamlines the development process.
Blazor and Web Assembly:
With the release of Blazor Web Assembly, Blazor—the framework for creating interactive web applications with C# and .NET—has undergone development. This makes it possible to run C# code directly within a browser, providing client-side web developers with a strong substitute for JavaScript. Blazor’s Web Assembly integration has become popular for generating rich client-side experiences.
Serverless Computing with Azure Functions:
With Azure Functions setting the standard, serverless computing has become widely used in .NET development. With Azure Functions, developers can create scalable, event-driven applications without having to actively manage server infrastructure. This pattern is consistent with the industry-wide move toward microservices and serverless architectures.
Microservices Architecture and gRPC:
Microservices are still a popular architectural pattern, and gRPC has become the standard for microservices-to-microservices communication. Because of gRPC’s effectiveness, language-neutrality, and bidirectional communication support, it’s becoming more and more common in .NET Core projects to create scalable and effective microservices.
Entity Framework Core Advancements:
The ORM framework for .NET, Entity Framework Core, has been continuously improved. Better performance, new features, and more flexibility in data mapping and querying are all advantageous to developers. Entity Framework Core continues to be an essential part of the .NET ecosystem as businesses aim for effective data access.
DevOps Integration and CI/CD Practices:
The incorporation of DevOps practices into .NET development workflows has become commonplace. Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines automate testing, build processes, and deployment, resulting in faster and more reliable software delivery.
AI and Machine Learning in .NET:
Artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities are increasingly being integrated into .NET applications. .NET developers can use ML .NET, an open-source framework, to seamlessly integrate machine learning models into their applications. This trend reflects the increasing demand for intelligent, data-driven solutions.
Containerization and Docker:
Containerization with Docker has become a standard in .NET development. Docker containers make it easy to package, deploy, and scale applications, which developers appreciate. Container orchestration tools such as Kubernetes help to streamline the management of containerized .NET applications.
Conclusion:
The .NET and .NET Core ecosystems are thriving and constantly evolving to meet the needs of modern software development. As developers embrace trends such as .NET 6, cross-platform development with .NET MAUI, serverless computing, microservices architecture, and emerging technologies such as Blazor Web Assembly, they position themselves to create scalable, efficient, and creative solutions. Staying informed about these trends enables developers to make informed decisions and prepares them for the exciting developments that lie ahead in the world of .NET.
Begin your Journey Today,
for Training, Contact via Call/WhatsApp :+91 90427 10472
How to Get Ready for a Dotnet Interview
Microsoft’s Dotnet framework is widely used for developing robust and scalable applications. Preparing for a Dotnet interview, whether you’re a seasoned developer or a recent graduate, necessitates a thorough understanding of the framework, its components, and best practices. In this article, we’ll go over key areas to concentrate on and offer practical advice to help you succeed in your Dotnet interview.
Understand the Fundamentals:
Before moving on to more advanced topics, make sure you understand fundamental concepts like Common Language Runtime (CLR), Common Type System (CTS), and Common Intermediate Language (CIL). Examine object-oriented programming principles, which are essential for Dotnet development.
Master Core Technologies:
C# Language Proficiency:
C# is the primary language used in Dotnet development, so brush up on it. Prepare to show your understanding of language features, inheritance, polymorphism, and exception handling.
ASP Dotnet and ASP Dotnet Core:
Learn the distinctions between ASP Dotnet and ASP Dotnet Core. Understand the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture, as well as routing and middleware.
ADO Dotnet and Entity Framework:
It is critical to have a solid understanding of ADO Dotnet for data access and Entity Framework for object-relational mapping. Prepare to talk about database connectivity, LINQ, and data modelling.
Explore Web Technologies:
Web API and RESTful Services:
Learn how to create and use Web APIs. Learn RESTful principles as well as how to design and implement scalable services.
Front-End Development:
Learn about front-end technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Knowledge of JavaScript frameworks such as Angular or React can be advantageous.
Look into Testing and Debugging in Depth:
Unit Testing:
Understand the significance of unit testing and be acquainted with testing frameworks such as NUnit or xUnit. Understand how to write efficient unit tests for your code.
Debugging Skills:
Demonstrate your ability to efficiently troubleshoot and debug code. Understand how to use Visual Studio’s debugging tools.
Explore Cloud Services:
Azure Services:
Many businesses use Microsoft Azure to host and manage applications. Understand Azure services such as Azure App Service, Azure Functions, and Azure SQL Database.
Security Best Practices:
Authentication and Authorization:
Learn about various authentication mechanisms such as OAuth and OpenID Connect. Understand how to use role-based access control (RBAC) to secure applications.
Secure Coding Practices:
Understand common security flaws and best practices for writing secure code. Learn how to defend against common threats such as SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Keep Up with the Latest Trends:
Latest versions updates:
Keep yourself updated on the latest versions of Dotnet, including Dotnet Core and be aware of new features and improvements.
Containerization and Microservices:
Learn about Docker containerization and the concept of microservices. Learn how these architectural patterns can benefit Dotnet applications.
Behavioral and Problem-Solving Questions:
Soft Skills:
Be prepared to answer behavioral questions about your communication, teamwork, and problem-solving abilities.
Coding Challenges:
Exercise your coding skills by solving algorithmic and real-world problems. LeetCode and HackerRank, for example, provide a variety of Dotnet-related challenges.
Conclusion:
Getting ready for a Dotnet interview necessitates a mix of technical knowledge, practical skills, and problem-solving abilities. You’ll be well-equipped to impress your interviewers and land that Dotnet development role if you focus on the key areas mentioned above and stay up to date on the latest trends. Best wishes!
Begin your Journey Today,
for Training, Contact via Call/WhatsApp :+91 90427 10472
Overview of C# and DotNet
Introduction:
The synergy between C# and the DotNet framework has become a cornerstone for building a wide range of applications, from desktop software to web services and cloud-based solutions, in the realm of software development. In this article, we’ll look at the capabilities, features, and versatility that C# and DotNet bring to the table, making them a dynamic programming duo.
C#: A Versatile and Modern Language:
A Quick Overview of C#:
Microsoft C# (pronounced “C sharp”) is a modern, object-oriented programming language. It combines the best features of C and C++ with the simplicity of Java, making it an excellent choice for developers looking for a powerful and expressive programming language.
Object-Oriented Paradigm:
C# adheres to the principles of object-oriented programming (OOP), emphasizing encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism. This enables developers to write modular, maintainable code, resulting in more efficient software design.
Type Safety and Memory Management:
C# is a statically-typed language, which means that variable types are known at compile time, reducing the likelihood of runtime errors. Automatic memory management via the garbage collector improves the language’s robustness.
Asynchronous Programming:
C# simplifies asynchronous programming with the introduction of the async and await keywords. This is especially important when developing responsive applications that can handle concurrent tasks without blocking.
DotNet: A Unified Development Platform
Introduction to the DotNet Framework:
Microsoft’s DotNet framework is a comprehensive platform for developing, deploying, and running applications. It provides a consistent development environment for a wide range of applications, including web, mobile, desktop, cloud, and gaming.
Common Language Runtime (CLR):
The Common Language Runtime (CLR), which manages the execution of DotNet programs, is at the heart of the DotNet framework. It has functions like automatic memory management, exception handling, and security.
Unified Type System:
The DotNet framework has a unified type of system in which all types, whether built-in or user-defined, derive from a single root (System.Object). This unity promotes interoperability and code reuse across the DotNet ecosystem’s various languages.
Extensive Class Library:
DotNet includes a large class library with pre-written code for common programming tasks. The Base Class Library (BCL) is a library that simplifies development by providing a wide range of functionalities without the need to reinvent the wheel.
Building Applications with C# and DotNet:
Desktop Applications with WPF:
C# is frequently used to develop Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) applications, which allow for the creation of feature-rich and visually appealing desktop software.
Web Development with ASP DotNet:
ASP DotNet, a component of the DotNet framework, allows developers to use C# to create dynamic and scalable web applications. ASP DotNet provides a strong framework for developing APIs and full-stack web applications.
Cross-Platform Development with DotNet Core and DotNet 5/6/7:
Recent DotNet ecosystem advancements, such as DotNet Core and the subsequent DotNet 5, DotNet 6, and DotNet 7, have expanded C#’s capabilities to embrace cross-platform development. Developers can now create applications that run on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Mobile App Development with Xamarin:
C# is used in mobile app development by Xamarin, a framework that allows developers to create cross-platform mobile apps for iOS, Android, and Windows using a single codebase.
Conclusion:
C# and DotNet are modern software development pillars, providing a versatile and unified platform for developing a wide range of applications. Whether you are an experienced developer or just starting out, exploring the capabilities of C# and DotNet opens up a world of possibilities. The continuous evolution of these technologies ensures that developers have the tools they need to stay ahead of the ever-changing software development landscape. Remember that the journey is just as rewarding as the destination as you delve deeper into the worlds of C# and DotNet.
Have fun coding!
Begin your Journey Today,
for Training, Contact via Call/WhatsApp :+91 90427 10472
Developing ASP.NET Core MVC Web Applications:
Introduction:
Creating dynamic and interactive web pages using the ASP.NET Core framework is required when developing ASP.NET Core MVC (Model-View-Controller) web applications. Model, View, and Controller (MVC) is a design pattern that divides an application into three main components: Model, View, and Controller. ASP.NET Core MVC is a lightweight, cross-platform, open-source framework for building modern, scalable web applications.
Here is a step-by-step tutorial for creating ASP.NET Core MVC web applications:
1. Install Prerequisites:
As your development environment, install Visual Studio or use Visual Studio Code.
Install the.NET SDK from the Microsoft website:
https://dotnet.microsoft.com/download
2. Create a new ASP.NET Core MVC project as follows:
Open Visual Studio and choose “Create a new project.”
Select “ASP.NET Core Web App” and then “ASP.NET Core with MVC” as the template.
Configure the project parameters and then click “Create.”
3. Understand the Project Structure:
Look into the project structure to learn about the key components:
Controllers: Controllers are responsible for handling user input and orchestrating interactions between the model and the view.
Views: Present information to the user and collect user input.
Models: Represent the application’s data and business logic.
4. Define Models:
Model classes should be created to represent the data entities in your application.
Data annotations can be used to validate data and define metadata.
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Name { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
5. Create Controllers:
To handle user requests and interact with models, create controllers.
Define controller actions to respond to specific HTTP requests.
public class ProductController : Controller
{
public IActionResult Index()
{
// Retrieve and return a list of products
return View(products);
}
public IActionResult Details(int id)
{
// Retrieve a specific product by id and return it
return View(product);
}
}
6. Develop Views:
To define the presentation layer, create view files (.cshtml).
To display dynamic content, use Razor syntax to embed C# code within HTML.
@model List<Product>
<h2>Product List</h2>
<ul>
@foreach (var product in Model)
{
<li>@product.Name - $@product.Price</li>
}
</ul>
7. Configure Routing:
Define routes in the Startup.cs file to map URLs to controller actions.
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
8. Handle Form Submissions:
In controllers, use the HttpPost attribute to handle form submissions.
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Create(Product product)
{
// Validate and save the new product
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
9. Implement Data Access:
To interact with databases, use Entity Framework Core or other data access technologies.
10. If desired, include authorization and authentication:
Authenticate and authorize users in accordance with the specifications of your application.
11. Test Your Application:
Run your application locally and verify various scenarios to test it.
12. Publish Your Application:
Publish your ASP.NET Core MVC application to a cloud platform or hosting environment.
Note: Always refer to the official ASP.NET Core documentation for more information on each stage of development: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/
Learn DOTNET Core Online
Overview of DOTNET Core: A Contemporary Framework for Cross-Platform Development
Microsoft created the free, open-source, cross-platform DOTNET Core framework to help developers create contemporary, scalable applications. With its modular design and lightweight architecture, it offers a substantial departure from the conventional DOTNET Framework and supports a broad variety of application kinds. We’ll go over the main benefits and features that make DOTNET Core a desirable option for developers in this introduction.
Principal attributes:
1. Cross-Platform Interoperability: With the help of DOTNET Core, programmers can create and execute apps for Windows, Linux, and macOS. For contemporary development scenarios, where applications must be deployed on various environments, cross-platform support is essential.
2. High-performance and modular: Because DOTNET Core is modular by design, developers can include only the parts that are required for their application. Its modularity makes it perfect for microservices and cloud-native apps because it reduces footprint and speeds up startup times.
3. Community-driven and Open Source: The framework is being developed as an open-source project to encourage community contributions and collaboration. This openness encourages transparency and creativity while guaranteeing that developers can take an active role in the framework’s evolution.
4. Combined Platform for Various Tasks: Cloud-native microservices, cross-platform desktop apps with Xamarin, and web development with ASP DOTNET Core are just a few of the workloads that can be combined into one cohesive platform with DOTNET Core. Because of its adaptability, developers can use the same set of tools and libraries for various kinds of applications.
5. Modern Development Practices Support: DOTNET Core supports contemporary development practices such as Docker containerization, continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD), and microservices architecture. These characteristics make it ideal for developing and deploying scalable, cloud-ready applications.
6. Comparative Versioning: In contrast to the conventional DOTNET Framework, side-by-side versioning is supported by DOTNET Core. This enables applications to use the version of the runtime and libraries that they were built with by allowing multiple versions to coexist on the same machine.
DOTNET Core components include:
1. DOTNET Core Runtime: The Common Language Runtime (CLR) and Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation are two of the runtime’s key components that are required to run DOTNET Core applications.
2. Core Libraries for.NET: These libraries offer common functionality for applications built with DOTNET Core. They consist of networking, file I/O, data structures, and algorithms, among other things.
3. ASP DOTNET Core: A cross-platform, high-performance framework for creating contemporary, cloud-based, and internet-connected apps is called ASP DOTNET Core. It’s frequently utilized for creating microservices, APIs, and web apps.
4. Entity Framework Core: An open-source, lightweight, and extensible object-relational mapping (ORM) framework is called Entity Framework Core. It makes working with databases using C# objects easier for developers by streamlining persistence and data access.
Getting Started:
Setting up your development environment, starting a new project, and learning the core principles of ASP DOTNET Core are the first steps in getting started with the framework. Here is a step-by-step tutorial to get you started with ASP DOTNET Core web application development.
Step 1: Install Prerequisites
Make sure the following is installed on your computer before you begin:
a.) DOTNET SDK: The DOTNET SDK can be downloaded and installed from the official DOTNET website: Get the DOTNET SDK here.
b.) Code Editor: Select a code editor for your project. Although Visual Studio Code is a well-liked option, you are free to use any other code editor of your choosing.
Step 2: Create a New Project for ASP DOTNET Core
To start a new ASP DOTNET Core project, launch a terminal or command prompt and type the following commands:
# Create a new folder for your project
mkdir MyFirstAspNetCoreApp
cd MyFirstAspNetCoreApp
# Create a new ASP DOTNET Core web application
dotnet new web -n MyFirstAspNetCoreApp
Step 3: Explore the Project Structure
Go to the project folder and examine the project hierarchy. Important documents and directories consist of:
Program.cs: Program.cs is the application’s entry point.
Startup.cs: Startup.cs is responsible for configuring the application’s services and middleware.
wwwroot: Static files (CSS, JavaScript, images) are stored in the wwwroot directory.
Controllers: The controllers that handle requests are listed here.
Views: This collection contains the views that define the user interface.
Models: Contains the data models that the application employs.
Step 4: Run the Program
To build and run the application, use the following command:
dotnet run
Navigate to https://localhost:1001 (or http://localhost:1002) in a web browser. The default ASP DOTNET Core welcome page should appear.
Step 5: Make a Simple Modification
In your code editor, open the project. There is an action method called Index in the Controllers/HomeController.cs file. Modify the ViewBag’s content.Message to another entity. As an example:
public IActionResult Index()
{
ViewBag.Message = “Hello, ASPDOTNETCore!”;
return View();
}
When you save the file, the web application will reload with your changes.
Step 6: Also, Understand the Fundamentals
Explore the following fundamental concepts:
Routing: Learn about URL routing in ASP DOTNET Core. Route configurations can be found in the Startup.cs file.
Views and Razor Pages: Discover how to make views with Razor syntax. Static files can be found in the Views and wwwroot folders.
Dependency Injection: Learn how to configure dependency injection in ASP DOTNET Core. For service registration, look in the Startup.cs file.
Middleware: Discover the elements of middleware and how the Startup.cs file configures them.
As you gain more familiarity with the fundamentals of ASP DOTNET Core development, you should also think about exploring more complex subjects like database access, authentication, and deployment.
Begin your journey today, for Training / Technical Support, Contact +91 90427 10472
DOTNET Online Training in Chennai
Unleashing Your DOTNET Software Development Potential
Do you want to learn about versatile and powerful software development – DOTNET & SQL? There is no need to look any further! Our Maria Academy is intended to provide you with the skills and knowledge required to thrive in the fast-paced field of application development.
About DOTNET (.NET)
Microsoft’s .NET framework is a robust and widely used framework for developing a wide range of applications, from desktop and web applications to mobile and cloud solutions. The demand for skilled .NET developers is increasing as the technology industry evolves.
About SQL
SQL, or Structured Query Language, is a programming language that is standardized for managing and manipulating relational databases. It includes commands for querying data, inserting records, updating information, and creating database structures. SQL is required for interacting with databases in a variety of applications, allowing for the structured and organized storage, retrieval, and manipulation of data. Its syntax is consistent across various database management systems, making it a universal database communication language. A solid understanding of SQL is essential in the world of data management and application development, whether you’re a developer, data analyst, or database administrator.
Why Should You Take .NET Online Training?
Versatility: Because .NET supports the development of a wide range of applications, it is a popular framework for a wide range of projects.
Industry Importance: Many large enterprises and organizations rely on .NET to build scalable and secure applications, resulting in many job opportunities.
Cross-Platform Development: .NET Core allows developers to create applications that run on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Excellence in Web Development: ASP.NET, a component of the .NET framework, is a leading technology for developing powerful and dynamic web applications.
What Our Training Provides:
Comprehensive Curriculum: Our training covers the entire scope of .NET, from fundamental concepts to advanced topics, ensuring you’re ready for real-world projects.
Hands-on Projects: Gain practical experience by working on real-world projects and applying what you’ve learned throughout the course.
Flexibility: Our online format allows you to learn at your own pace, working around your hectic schedule.
Interactive Learning: To improve your comprehension and get answers to any questions, participate in interactive sessions, debates, and Q&A sessions.
Professional Teachers: Learn from professionals in the field who have a great deal of .NET development experience and gain insightful advice.
Who Needs to take:
IT Specialists Seeking Professional Development
Aspiring Programmers
Web Designers
Software Developers
Join Us to Advance Your Career!
Begin your journey to becoming a skilled .NET developer. Our .NET Online Training in Chennai is your ticket to mastering the skills that industry leaders are looking for. Are you prepared to shape your future in software development? Enroll right away!
for Training / Technical Support in .NET, Contact +91 90427 10472
DOTNET Online Training in Coimbatore
SQL and .NET (sometimes spelled DOTNET) are two separate technologies that are commonly utilized in software development. SQL, which stands for Structured Query Language, is a powerful computer language that was created primarily for maintaining and manipulating relational databases. It provides a standardized approach for developers to accomplish operations including accessing data, entering records, updating information, and designing database structures.
.NET, on the other hand, is a framework developed by Microsoft for building various types of applications, including desktop, web, and mobile applications. It provides a comprehensive set of libraries and tools for developers to build, deploy, and run applications. .NET supports multiple programming languages, including C#, F#, and Visual Basic, and it includes a runtime, a set of libraries, and development tools.
While SQL is primarily focused on working with databases and managing data, .NET is a broader framework that covers a wide range of application development aspects. However, it’s common for developers to use SQL in conjunction with .NET when building applications that require interaction with a database.
In a typical scenario, a .NET application may use SQL to store and retrieve data from a relational database. This interaction is often facilitated by using an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework, such as Entity Framework, which is a popular component of the .NET ecosystem. Entity Framework allows developers to work with databases using object-oriented principles, making it easier to integrate database operations into .NET applications.
Do you want to know if.NET is still in demand?
There is no need to look any further! .NET is an open-source web framework that is one of the most popular web application development frameworks for creating dynamic websites. With such promising future growth potential, it’s no surprise that professionals with prior experience in this industry are in high demand today. Keep your.NET skills sharp to stay ahead of the curve!
.NET is a framework that provides programming principles for creating a wide range of applications, from web-based to mobile-based. It supports a variety of programming languages, including C#, VB.NET, C++, F#, and others. So, when working with.NET, code is essential. Continue to experiment and study to become a skilled.NET developer!
.NET is the primary framework for developing Windows-based applications. This is due to the fact that.NET is a local framework bundled with Windows that makes it easier for programmers to construct applications. Furthermore, many programmers find it easier to construct web applications in.NET than in Java.
The.NET Framework’s ability to create a highly secure environment for applications is well known. It includes a variety of security mechanisms to ensure maximum protection. One of these mechanisms is the built-in Windows authentication system, which enables developers to create secure and safe applications with ease. This authentication system ensures that only authorized users have access to the application, improving its overall security.
Furthermore, the.NET Framework includes a set of cryptography classes that are essential for protecting sensitive data. These classes enable encryption and decryption, which improves data security. Developers can use these cryptography classes to implement strong encryption algorithms that effectively protect data during transmission and storage. This ensures that confidential data remains private and out of reach of unauthorized individuals.
As a result, by incorporating a wide range of security features, the.NET Framework enables developers to prioritize data protection and mitigate potential security risks when developing applications.
“Unlock Your True Potential with Maria Academy – Unleashing Excellence through Education”
Are you ready to elevate your skills and achieve your goals? Look no further than Maria Academy, the leading training institute dedicated to nurturing talent and empowering individuals to reach their full potential. Our team of seasoned professionals, industry experts, and passionate educators is committed to providing exceptional learning experiences that pave the way for success.
Discover a wide range of courses tailored to meet the demands of today’s competitive market. From professional development programs, technical certifications, to specialized workshops, Maria Academy offers comprehensive training solutions that equip you with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in your chosen field.
Join our vibrant community of learners and engage in interactive sessions that foster collaboration, critical thinking, and innovation. At Maria Academy, we believe in providing more than just theoretical knowledge; we strive to ignite your passion, creativity, and confidence, enabling you to thrive in any professional setting.
Take the first step towards a brighter future. Enrol now at Maria Academy and embark on a transformative educational journey that will shape your career and change your life.”
With Maria Academy’s online course, you can unlock a world of career opportunities in SQL, C#, and Dot Net Technology. Whether you’re an experienced programmer looking to expand your knowledge or a beginner venturing into object-oriented programming, our C#.NET course will take you to the next skill level. Our team of experienced instructors will guide you through the intricacies of C#, helping you discover its limitless potential.
But that’s not all – we also offer comprehensive SQL training to transform you into a proficient database professional. Even advanced engineers can benefit from refreshing their knowledge with our SQL courses. And it’s not just for engineers; business analysts can also capitalize on the opportunity to learn about emerging trends and markets.
At Maria Academy, we take pride in our interactive training sessions. Our enthusiastic trainers will delve into real-world problems and provide practical solutions. What sets us apart is our commitment to hands-on programming, allowing students to improve their skills through practical exercises. Rest assured; our trainers have a minimum of five years of industry experience.
Our meticulously crafted curriculum covers the entire C# learning process. You’ll have the chance to put your programming skills to the test with practical exams and periodic exercises. By the end of the training, we guarantee that you’ll be able to tackle real-world scenarios with confidence.
When it comes to placement assistance, course quality, syllabus coverage, and practical application, we stand tall as the premier C#.NET Training Provider in India. Choose us and unlock your true programming potential.
Recent Posts
Categories
- All
- Angularjs training in Chennai
- ASP.NET Core
- dot net training
- dot net training in chennai
- dotnet full stack developer
- Free dotnet training
- information on dotnet
- Learn Java in chennai
- Learn Python at Karaikudi
- learn python online
- learn python online from chennai
- Linq Queries in .net
- mutual funds
- MVC Training Tutorials
- PHP Training in Chennai
- pmp training online
- power apps online training
- Python Training Online
- share market
- Sharepoint framework online training
- SharePoint Freelancers in Chennai
- software testing
- spfx online training
- Stock market
- Uncategorized

